

al-Jahiz’s Book of Animals: The transcendent value of disgust
by Jeannie MillerPublished on: 11th August 2016
Jeannie Miller, an assistant professor in the department of near & Middle Eastern civilizations, is working on a manuscript examining The Book of Animals by al-Jahiz, a ninth-century Arabic writer and polymath. Al-Jahiz saw himself as a theologian and natural scientist, but is often miscast because of the risqué nature of some of his prose.

Editorial Note: Written by Jeannie Miller, first published in the University of Toronto website and composed by Cem Nizamoglu for 1001 Inventions and Muslim Heritage websites with additional images and further information.
***
The transcendent value of disgust: U of T’s Jeannie Miller offers a new perspective on an Arabic scholar
Jeannie Miller is making a big impact with a new perspective on some very old prose.
Miller, an assistant professor in the department of near & Middle Eastern civilizations, is working on a manuscript examining The Book of Animals by al-Jahiz, a ninth-century Arabic writer and polymath. Al-Jahiz saw himself as a theologian and natural scientist, but is often miscast because of the risqué nature of some of his prose.
Jeannie Miller (third from left) with students Wajih Ahmed, Oona Nadler and Muhammad Ansab (Photo by Diana Tyszko) (Source)
“He sometimes gets placed as an entertaining literary figure, as opposed to a religious thinker, which I think is wrong,” says Miller, whose forthcoming book is entitled Performative Inquiry: How Rhetoric Produced an Abbasid Natural Science.
“These things were not necessarily opposed in the ninth century. By classifying al-Jahiz that way, one misrepresents the history of Islam by removing his entertaining work from that history.”
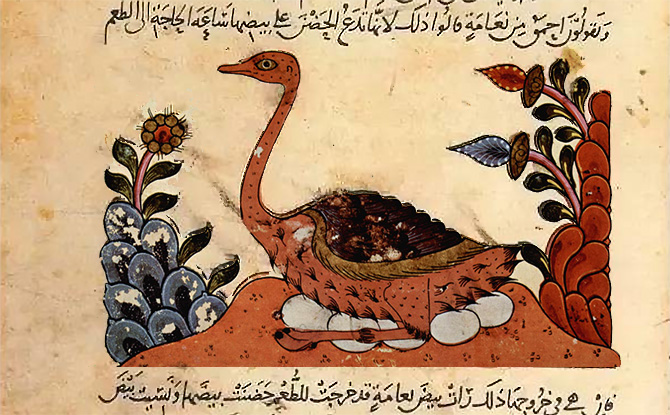

Page from the Book of Animals by African Arab naturalist and evolutionist al Jahiz. Kitab al Hayawan (Book of Animals). Ninth Century. Basra. by Abu Uthman Al-Jaahiz (Image Source)
The Book of Animals was written “in service to God,” says Miller, and partly in response to Aristotle’s biology books. In it, al-Jahiz exhibits an “exciting and very inclusive” approach to humanity. Using pigeons as an analogy, for example, he observes that there seem to be many natural forms of sexuality, including homosexuality in males and females, as well as varying preferences regarding domination.
“Much of the Book of Animals is dedicated to arguing against people who thought that exceptional people and animals were monstrous or scary. Like most intellectuals of his time, he was an elitist and did not treat everyone equally — but he did treat all kinds of people as natural results of God’s creation,” says Miller, a former Fulbright scholar who joined the U of T faculty in 2013 after doing her undergraduate degree at Harvard University and her doctorate at New York University.
“I’ve always been interested in works that blend literature and science. For this project, I wanted to set aside modern divisions between science and literature, and between entertainment and religion, and just ask what al-Jahiz was trying to accomplish, and why he felt it had to be done this way,” Miller says. “He says his goal is to show how wondrous divine creation is, but was it really necessary to spend half a volume citing poetry about excrement and the perversions of the dung beetle?”
Miller’s book will make the case that in fact al-Jahiz did think it was necessary to examine feelings of repulsion and attraction, through poetry and rational argument, in order to fully understand the place of humans in God’s creation. “He wanted to bring together every way of knowing and understanding the world God created, including our innate reactions of disgust or pleasure.”

The Crocodile from The Book of Animals by Al-Jahiz Credit: © Veneranda Biblioteca Ambrosiana, Milan, Italy/Bridgeman Images (Image Source)
This was very likely a product of his exposure to the rhetorical debates practised by his theology teachers, adds Miller. “They weren’t just engaging in dialectic — they were also citing poetry, and recounting anecdotes to make points about the natural world.”
Paper had been introduced to the Muslim world around 800 AD and al-Jahiz responded to this new technological opportunity by writing large compilations as a way to preserve, defend, and theorise some of those rhetorical debate practices.
Miller notes al-Jahiz was a foundational writer in the “adab” genre, and that even though this type of writing was often full of “obscene stories and dirty jokes,” it was also often religious in nature. In fact, many adab writers were religious scholars.
“Adab texts are obscene and they are religious, and I don’t think people felt a lot of problems with that at the time,” says Miller, who studied Arabic in Ethiopia and in Syria just before the war.
Modern editions of those texts, published both by European and Arab presses, have at certain times removed passages deemed too sexual or homoerotic, but this didn’t happen to al-Jahiz, she says.
Arabic texts are worthy of being studied with the care, attention and creativity afforded English literary heritage, adds Miller, who also speaks some French, Italian, German and Hebrew.
“Just allowing English speakers access to the richness, complexity and diversity of the Arabic heritage is a small contribution to combatting Islamophobia.”
This article has been taken from University of Toronto website with permission.
 Imaginary potrait of Al-Jahiz (Source) |  Qatar Stamp of Al-Jahiz (Source) |
Related Muslim Heritage Articles
- Al-Jahiz – Abū ʿUthman ʿAmr ibn Baḥr al-Kinānī al-Baṣrīz
- It’s Time to Herald the Arabic Science That Prefigured Darwin and Newton
- Black History Month: African contributions to Muslim Civilisation
- Animal Care
- Kalila wa-Dimna
- Anatomy of the Horse in the 15th Century
- Cats in Islamic Culture:
 A lion eating the entrails of the carcass of a cow. The drawing fits the text: “The lion is the king of the beasts of prey, and it eats carcasses, and it begins by drinking the blood, then it opens the stomach and eats what is in it of food and saliva and the intestines together with the evacuation” Al-Jahiz, Kitab al-hayawan (The Book of Animals ), Cairo, Egypt, Seven volumes, 1323-1324 H. Mehemet Bayrakdar said: “The Kitab Al-Hayawan was the object of many studies, and had great influence upon later Muslim scientists, and via them upon European thinkers (especially upon Lamarck and Darwin). And it became the source for later books on zoology. Al-Jahiz’s many sentences are quoted by Ikhwan al-Safa and Ibn Miskawayh, and many passages are quoted by Zakariyya’ al-Qazwini (1203-1282) in his ‘Aja’ib al-Makhluqat, and by Mustawfi al-Qazwini (1281- ?) in his Nuzkat al-Qulub; and al-Damiri in his Hayat al-Hayawan‘ , and still continues to inspire the scientists today. For instance, Professor. Dr. R. Kruk whose inaugural lecture on “A Map of a cat” was also inspired by Islamic manuscripts and scientific references including Kitab Al-Hayawan. These books also had the role of a cultural drive for the progress of research in modern science in zoology, biology, evolutionary theories, medicine, veterinary, anatomy, etc.”
A lion eating the entrails of the carcass of a cow. The drawing fits the text: “The lion is the king of the beasts of prey, and it eats carcasses, and it begins by drinking the blood, then it opens the stomach and eats what is in it of food and saliva and the intestines together with the evacuation” Al-Jahiz, Kitab al-hayawan (The Book of Animals ), Cairo, Egypt, Seven volumes, 1323-1324 H. Mehemet Bayrakdar said: “The Kitab Al-Hayawan was the object of many studies, and had great influence upon later Muslim scientists, and via them upon European thinkers (especially upon Lamarck and Darwin). And it became the source for later books on zoology. Al-Jahiz’s many sentences are quoted by Ikhwan al-Safa and Ibn Miskawayh, and many passages are quoted by Zakariyya’ al-Qazwini (1203-1282) in his ‘Aja’ib al-Makhluqat, and by Mustawfi al-Qazwini (1281- ?) in his Nuzkat al-Qulub; and al-Damiri in his Hayat al-Hayawan‘ , and still continues to inspire the scientists today. For instance, Professor. Dr. R. Kruk whose inaugural lecture on “A Map of a cat” was also inspired by Islamic manuscripts and scientific references including Kitab Al-Hayawan. These books also had the role of a cultural drive for the progress of research in modern science in zoology, biology, evolutionary theories, medicine, veterinary, anatomy, etc.”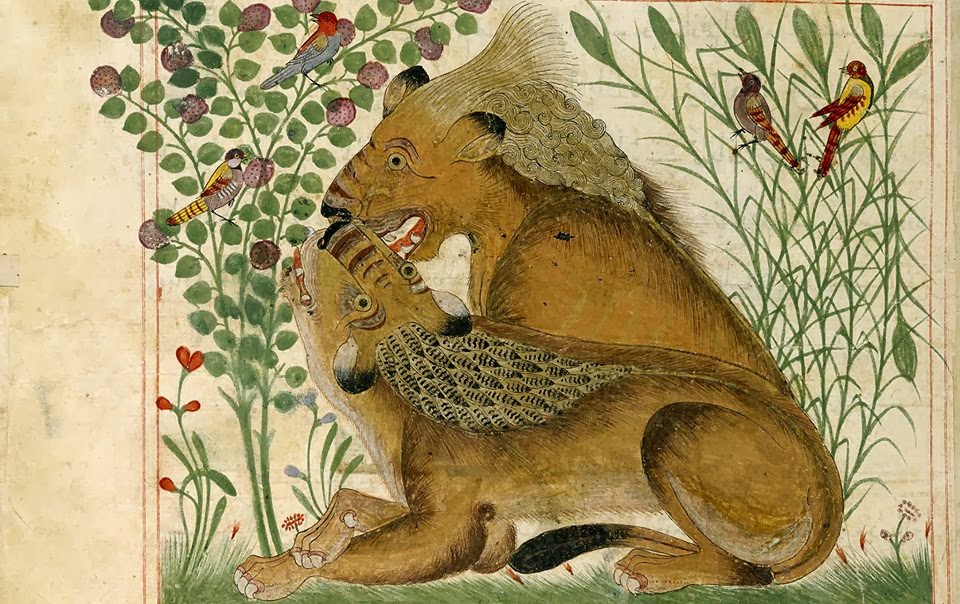
Inspired Ibn Bakhtishu’s Manafi’ al-Hayawan (Book on Animals), dated 12th century. Captions appear in Persian language. (Source)
These books not only covered a specific subject as scientific textbooks, but also acted as enlightening guides just like most other early Muslim scientific books.
An example is a line from Al-Jahiz’s Kitab Al-Hayawan:
 | …and the cat profits so much from its resemblance to the king of beasts that one way of dealing with approaching war elephants is to release a quantity of cats from a bag.” |
From Cats in Islamic Culture by Cem Nizamoglu
***

Al-Ǧāḥiẓ/Jahiz, Kitāb al-ḥayawān (Book of the animals), Syria, 15th C. Milan, Biblioteca Ambrosiana, Ms. arab. B 54, f. 36 (Image Source)










.png)













No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario